PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
APPLICATIONS
FRUIT THINNING AGENTS
2-Chloroethyl phoshonic acid (Ethephon, Rhone-Poulenc)
1-Napthaleneacetic acid and its sodium and potassium salts (Fruitone N, AMVAC)
Isopropyl Ester of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid (Citrus Fix, ALCO)
N-(Phenyl)-1H-purine 6-amine (Accel, Abbott)
1-Napthyl (N-) methylcarbamate (Carbaryl, Rhone-Poulenc)
2-(Dimethylamino)-N-[[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]-2-oxoethanoimido- thioic acid methyl ester (Oxamyl, DuPont)
APPEARANCE
ACTIVE CONTENT
98.0% min
25kgs in fiber drum
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- Auxins
- 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid (CAS RN: 122-88-3)
- (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid (CAS RN: 94-75-7)
- 4-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)butyric acid (CAS RN: 94-82-6)
- Tris[2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)ethyl] phosphite (CAS RN: 94-84-8)
- 2-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid (CAS RN: 120-36-5)
- 2-(2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy)propanoic acid (CAS RN: 93-72-1)
- Indole-3-acetic acid (CAS RN: 87-51-4)
- Indole-3-butyric acid (CAS RN: 133-32-4)
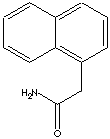
- 1-Naphthaleneacetamide (CAS RN: 86-86-2)
- 1-Naphthaleneacetic acid (CAS RN: 86-87-3)
- 1-Naphthol (CAS RN: 90-15-3)
- Naphthoxy acetic acid (CAS RN: 120-23-0)
- Naphthenic acid, inorganic salts (potassium, sodium)
- (2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxy) Acetic acid (CAS RN: 93-76-5)
- Antiauxins
- Clofibric acid (CAS RN: 882-09-7)
- 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic acid (CAS RN: 88-82-4)
Cytokinin is a N6-substituted adenines acting as phytohormones such as kinetin, zeatin, 6-isopentenyladenine, benzyl adenine. The principal functions are stimulate cell division in concert with auxin (cytokinesis) and influence the pathway of tissue differentiation (organogenesis). 6-Benzylaminopurine is the first generation synthetic cytokinin which elicits plant growth and development responses setting blossoms and stimulating fruit richness by stimulating cell division. Active cytokinin ingredients include:
- Adenine (CAS RN: 73-24-5)
- Adenine Hemisulfate salt (CAS RN: 321-30-2)
- 6-Benzylaminopurine (CAS RN: 1214-39-7(base), 162714-86-5(HCl)
- N-Benzyl-9-(2-tetrahydropyranyl)adenine (CAS RN: 2312-73-4)
- N-(2-Chloro-4-pyridyl)-N'-phenylurea (CAS RN: 68157-60-8)
- 6-(gamma,gamma-Dimethylallylamino)purine (CAS RN: 2365-40-4)
- 1,3-Diphenylurea (CAS RN: 102-07-8)
- Kinetin (CAS RN: 525-79-1 (base), 177966-68-6 (HCl)
- 1-Phenyl-3-(1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-yl) Urea (CAS RN: 51707-55-2)
- Zeatin (CAS RN: 13114-27-7)
- trans-Zeatin (CAS RN: 1637-39-4 (base), 6025-81-6 (HCl))
- trans-Zeatin riboside (CAS RN: 6025-53-2)
Other Plant Growth Regulators include:
- Abscisic acid (CAS RN: 21293-29-8)
- Ancymidol (CAS RN: 12771-68-5)
- Chlorocholine chloride (CAS RN: 999-81-5)
- Daminozide (CAS RN: 1596-84-5)
- 3,6-Dichloro-o-anisic acid (CAS RN: 1918-00-9)
- Gibberellic acid (CAS RN: 77-06-5)
- Gibberellic acid Potassium salt (CAS RN: 125-67-7)
- Gibberellin A4 (CAS RN: 468-44-0 ) and other gibberellins (more than 110 gibberellins are known)
- Glyphosate (CAS RN: 1071-83-6)
- Jasmonic acid (CAS RN: 3572-66-5)
- 1,3,5-Trihydroxybenzene (CAS RN: 108-73-6)